The content of a file that is called from a low-level interfaced routine to perform input and output is replaced with a program for I/O.
With the standard I/O functions GETC and PUTC, the functions that perform 1-character input and output, "charput," "charget" (_charput, _charget), are replaced with a program for debug console facilities, to perform input and output of data onto and from the Debug Console panel.
The I/O functions are listed below.
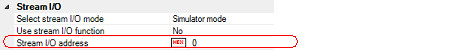
To implement I/O function of the simulator, first specify the I/O address in the [Stream I/O address] property within the [Stream I/O] [Simulator] category on the Property panel's [Debug Tool Settings] tab. This can be done by entering address expressions in the range of 0 to "last address of address space" directly from the keyboard.
Upon detecting "Branch to subroutine" instruction (BSR, JSR) to a specified address while executing instructions of the program, the simulator performs an I/O process using the contents of the R1 and R2 registers as parameters.
Therefore, be sure that the following setting is made in the program before an I/O process is performed.

For the content of the parameter block, see the description of each I/O function.
To access each parameter in the parameter block, make sure that an access is made in size of the relevant parameter.