5.3 Eventflags
The RI850V4 provides 32-bit eventflags as a queuing function for tasks, such as keeping the tasks waiting for execution, until the results of the execution of a given processing program are output.
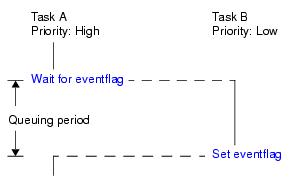
The following shows a processing flow when using an eventflag.
Figure 5-2 Processing Flow (Eventflag)
In the RI850V4, the method of creating an eventflag is limited to "static creation".
Eventflags therefore cannot be created dynamically using a method such as issuing a service call from a processing program.
Static event flag creation means defining of event flags using static API "CRE_FLG" in the system configuration file.
Bit pattern is set by issuing the following service call from the processing program.
-
set_flg,
iset_flg
These service calls set the result of logical OR operating the bit pattern of the eventflag specified by parameter
flgid and the bit pattern specified by parameter
setptn as the bit pattern of the target eventflag.
If the required condition of the task queued to the target eventflag wait queue is satisfied when this service call is issued, the relevant task is unlinked from the wait queue at the same time as bit pattern setting processing.
As a result, the relevant task is moved from the WAITING state (WAITING state for an eventflag) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
The following describes an example for coding this service call.
#include <kernel.h> /*Standard header file definition*/
#include <kernel_id.h> /*System information header file definition*/
void task (VP_INT exinf)
{
ID flgid = ID_FLG1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
FLGPTN setptn = 10; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
.........
set_flg (flgid, setptn); /*Set eventflag*/
.........
}
|
Note 1 If the bit pattern set to the target eventflag is B'1100 and the bit pattern specified by parameter
setptn is B'1010 when this service call is issued, the bit pattern of the target eventflag is set to B'1110.
Note 2 When the TA_WMUL attribute is specified for the target eventflag, the range of tasks to be checked on "whether issuing of this service call satisfies the required condition" differs depending on whether the TA_CLR attribute is also specified.
- When TA_CLR is specified
Check begins from the task at the head of the wait queue and stops at the first task whose required condition is satisfied.
- When TA_CLR is not specified
All tasks placed in the wait queue are checked.
A bit pattern is cleared by issuing the following service call from the processing program.
-
clr_flg,
iclr_flg
This service call sets the result of logical AND operating the bit pattern set to the eventflag specified by parameter
flgid and the bit pattern specified by parameter
clrptn as the bit pattern of the target eventflag.
The following describes an example for coding this service call.
#include <kernel.h> /*Standard header file definition*/
#include <kernel_id.h> /*System information header file definition*/
void task (VP_INT exinf)
{
ID flgid = ID_FLG1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
FLGPTN clrptn = 10; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
.........
clr_flg (flgid, clrptn); /*Clear eventflag*/
.........
}
|
Note If the bit pattern set to the target eventflag is B'1100 and the bit pattern specified by parameter
clrptn is B'1010 when this service call is issued, the bit pattern of the target eventflag is set to B'1110.
A bit pattern is checked (waiting forever, polling, or with timeout) by issuing the following service call from the processing program.
-
wai_flg
This service call checks whether the bit pattern specified by parameter
waiptn and the bit pattern that satisfies the required condition specified by parameter
wfmode are set to the eventflag specified by parameter
flgid.
If a bit pattern that satisfies the required condition has been set for the target eventflag, the bit pattern of the target eventflag is stored in the area specified by parameter
p_flgptn.
If the bit pattern of the target eventflag does not satisfy the required condition when this service call is issued, the invoking task is queued to the target eventflag wait queue.
As a result, the invoking task is unlinked from the ready queue and is moved from the RUNNING state to the WAITING state (WAITING state for an eventflag).
The WAITING state for an eventflag is cancelled in the following cases, and then moved to the READY state.
WAITING State for an Eventflag Cancel Operation
|
|
A bit pattern that satisfies the required condition was set to the target eventflag as a result of issuing set_flg.
|
|
A bit pattern that satisfies the required condition was set to the target eventflag as a result of issuing iset_flg.
|
|
Forced release from waiting (accept rel_wai while waiting).
|
|
Forced release from waiting (accept irel_wai while waiting).
|
|
The following shows the specification format of required condition
wfmode.
-
wfmode = TWF_ANDW
Checks whether all of the bits to which 1 is set by parameter
waiptn are set as the target eventflag.
-
wfmode = TWF_ORW
Checks which bit, among bits to which 1 is set by parameter
waiptn, is set as the target eventflag.
The following describes an example for coding this service call.
#include <kernel.h> /*Standard header file definition*/
#include <kernel_id.h> /*System information header file definition*/
void task (VP_INT exinf)
{
ER ercd; /*Declares variable*/
ID flgid = ID_FLG1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
FLGPTN waiptn = 14; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
MODE wfmode = TWF_ANDW; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
FLGPTN p_flgptn; /*Declares variable*/
.........
/*Wait for eventflag (waiting forever)*/
ercd = wai_flg (flgid, waiptn, wfmode, &p_flgptn);
if (ercd == E_OK) {
......... /*Normal termination processing*/
} else if (ercd == E_RLWAI) {
......... /*Forced termination processing*/
}
|
.........
}
|
Note 1 With the RI850V4, whether to enable queuing of multiple tasks to the event flag wait queue is defined during configuration. If this service call is issued for the event flag (TW_WSGL attribute) to which a wait task is queued, therefore, "E_ILUSE" is returned regardless of whether the required condition is immediately satisfied.
TA_WSGL: Only one task is allowed to be in the WAITING state for the eventflag.
TA_WMUL: Multiple tasks are allowed to be in the WAITING state for the eventflag.
Note 2 Invoking tasks are queued to the target event flag (TA_WMUL attribute) wait queue in the order defined during configuration (FIFO order or priority order).
Note 3 The RI850V4 performs bit pattern clear processing (0x0 setting) when the required condition of the target eventflag (TA_CLR attribute) is satisfied.
Note 4 If the WAITING state for an eventflag is forcibly released by issuing
rel_wai or
irel_wai, the contents of the area specified by parameter
p_flgptn will be undefined.
-
pol_flg,
ipol_flg
This service call checks whether the bit pattern specified by parameter
waiptn and the bit pattern that satisfies the required condition specified by parameter
wfmode are set to the eventflag specified by parameter
flgid.
If the bit pattern that satisfies the required condition has been set to the target eventflag, the bit pattern of the target eventflag is stored in the area specified by parameter
p_flgptn.
If the bit pattern of the target eventflag does not satisfy the required condition when this service call is issued, "E_TMOUT" is returned.
The following shows the specification format of required condition
wfmode.
-
wfmode = TWF_ANDW
Checks whether all of the bits to which 1 is set by parameter
waiptn are set as the target eventflag.
-
wfmode = TWF_ORW
Checks which bit, among bits to which 1 is set by parameter
waiptn, is set as the target eventflag.
The following describes an example for coding this service call.
#include <kernel.h> /*Standard header file definition*/
#include <kernel_id.h> /*System information header file definition*/
void task (VP_INT exinf)
{
ER ercd; /*Declares variable*/
ID flgid = ID_FLG1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
FLGPTN waiptn = 14; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
MODE wfmode = TWF_ANDW; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
FLGPTN p_flgptn; /*Declares variable*/
.........
/*Wait for eventflag (polling)*/
ercd = pol_flg (flgid, waiptn, wfmode, &p_flgptn);
if (ercd == E_OK) {
......... /*Polling success processing*/
} else if (ercd == E_TMOUT) {
......... /*Polling failure processing*/
}
.........
}
|
Note 1 With the RI850V4, whether to enable queuing of multiple tasks to the event flag wait queue is defined during configuration. If this service call is issued for the event flag (TW_WSGL attribute) to which a wait task is queued, therefore, "E_ILUSE" is returned regardless of whether the required condition is immediately satisfied.
TA_WSGL: Only one task is allowed to be in the WAITING state for the eventflag.
TA_WMUL: Multiple tasks are allowed to be in the WAITING state for the eventflag.
Note 2 The RI850V4 performs bit pattern clear processing (0x0 setting) when the required condition of the target eventflag (TA_CLR attribute) is satisfied.
Note 3 If the bit pattern of the target event flag does not satisfy the required condition when this service call is issued, the contents in the area specified by parameter
p_flgptn become undefined.
-
twai_flg
This service call checks whether the bit pattern specified by parameter
waiptn and the bit pattern that satisfies the required condition specified by parameter
wfmode are set to the eventflag specified by parameter
flgid.
If a bit pattern that satisfies the required condition has been set for the target eventflag, the bit pattern of the target eventflag is stored in the area specified by parameter
p_flgptn.
If the bit pattern of the target eventflag does not satisfy the required condition when this service call is issued, the invoking task is queued to the target eventflag wait queue.
As a result, the invoking task is unlinked from the ready queue and is moved from the RUNNING state to the WAITING state (WAITING state for an eventflag).
The WAITING state for an eventflag is cancelled in the following cases, and then moved to the READY state.
WAITING State for an Eventflag Cancel Operation
|
|
A bit pattern that satisfies the required condition was set to the target eventflag as a result of issuing set_flg.
|
|
A bit pattern that satisfies the required condition was set to the target eventflag as a result of issuing iset_flg.
|
|
Forced release from waiting (accept rel_wai while waiting).
|
|
Forced release from waiting (accept irel_wai while waiting).
|
|
Polling failure or timeout.
|
|
The following shows the specification format of required condition
wfmode.
-
wfmode = TWF_ANDW
Checks whether all of the bits to which 1 is set by parameter
waiptn are set as the target eventflag.
-
wfmode = TWF_ORW
Checks which bit, among bits to which 1 is set by parameter
waiptn, is set as the target eventflag.
The following describes an example for coding this service call.
#include <kernel.h> /*Standard header file definition*/
#include <kernel_id.h> /*System information header file definition*/
void task (VP_INT exinf)
{
ER ercd; /*Declares variable*/
ID flgid = ID_FLG1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
FLGPTN waiptn = 14; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
MODE wfmode = TWF_ANDW; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
FLGPTN p_flgptn; /*Declares variable*/
TMO tmout = 3600; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
.........
/*Wait for eventflag (with timeout)*/
ercd = twai_flg (flgid, waiptn, wfmode, &p_flgptn, tmout);
if (ercd == E_OK) {
......... /*Normal termination processing*/
} else if (ercd == E_RLWAI) {
......... /*Forced termination processing*/
} else if (ercd == E_TMOUT) {
......... /*Timeout processing*/
}
.........
.........
}
}
|
Note 1 With the RI850V4, whether to enable queuing of multiple tasks to the event flag wait queue is defined during configuration. If this service call is issued for the event flag (TW_WSGL attribute) to which a wait task is queued, therefore, "E_ILUSE" is returned regardless of whether the required condition is immediately satisfied.
TA_WSGL: Only one task is allowed to be in the WAITING state for the eventflag.
TA_WMUL: Multiple tasks are allowed to be in the WAITING state for the eventflag.
Note 2 Invoking tasks are queued to the target event flag (TA_WMUL attribute) wait queue in the order defined during configuration (FIFO order or priority order).
Note 3 The RI850V4 performs bit pattern clear processing (0x0 setting) when the required condition of the target eventflag (TA_CLR attribute) is satisfied.
Note 4 If the event flag wait state is cancelled because
rel_wai or
irel_wai was issued or the wait time elapsed, the contents in the area specified by parameter
p_flgptn become undefined.
Note 5 TMO_FEVR is specified for wait time
tmout, processing equivalent to
wai_flg will be executed. When TMO_POL is specified, processing equivalent to
pol_flg /
ipol_flg will be executed.
5.3.5 Reference eventflag state
An eventflag status is referenced by issuing the following service call from the processing program.
-
ref_flg,
iref_flg
Stores eventflag state packet (ID number of the task at the head of the wait queue, current bit pattern, etc.) of the eventflag specified by parameter
flgid in the area specified by parameter
pk_rflg.
The following describes an example for coding this service call.
#include <kernel.h> /*Standard header file definition*/
#include <kernel_id.h> /*System information header file definition*/
void task (VP_INT exinf)
{
ID flgid = ID_FLG1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/
T_RFLG pk_rflg; /*Declares data structure*/
ID wtskid; /*Declares variable*/
FLGPTN flgptn; /*Declares variable*/
ATR flgatr; /*Declares variable*/
.........
ref_flg (flgid, &pk_rflg); /*Reference eventflag state*/
wtskid = pk_rflg.wtskid; /*Reference ID number of the task at the */
/*head of the wait queue*/
flgptn = pk_rflg.flgptn; /*Reference current bit pattern*/
flgatr = pk_rflg.flgatr; /*Reference attribute*/
.........
}
|