This section explains how to create the ROMized load module file.
The -rom option is used for ROMization. The code is as follows.
When the function to automatically allocate sections is not specified in the linker, the addresses of the initial-value section and destination section need to be specified by the -start option. When the function to automatically allocate sections is specified in the linker, addresses do not have to be specified by the -start option.
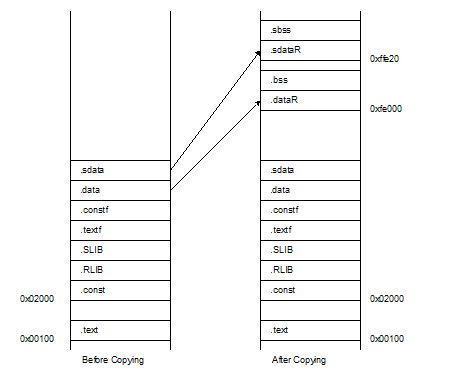
It is assumed that the user program contains sections .text, .textf, .RLIB, .SLIB, .const, .constf, .data, .sdata, .stack_bss, .bss, and .sbss. When locating .text at address 0x100, .const at address 0x2000, reallocation attribute DATA and BSS sections at address 0xfe000, reallocation attribute SDATA and SBSS sections at address 0xffe20 at program execution, the code will be as follows.
-start=.text/100 -start=.const,.RLIB,.SLIB,.textf,.constf,.data,.sdata/2000 -start=.dataR,.bss,.stack_bss/FE000 -start=.sdataR,.sbss/FFE20 -rom=.data=.dataR,.sdata=.sdataR |
The section names .dataR and .sdataR to which data is to be copied can be different names but they need to match the code in the startup routine. At program execution, data is copied from .data to .dataR and from .sdata to .sdataR, and .bss and .sbss are initialized before they are used.
An image of this operation is shown below.