The RX CPU can handle four types of data: integer, floating-point, bit, and string.
An integer can be signed or unsigned. For signed integers, negative values are represented by two's complements.
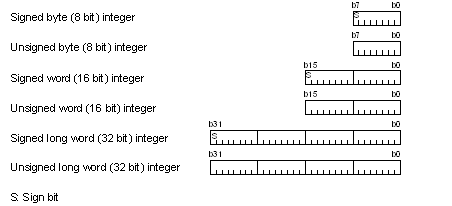
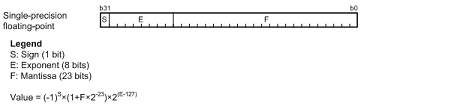
Floating-point support is for the single-precision floating-point type specified in IEEE754; operands of this type can be used in eight floating-point operation instructions: FADD, FCMP, FDIV, FMUL, FSUB, FTOI, ITOF, and ROUND.
Since products of the RX200 Series do not support instructions for floating-point operations, the floating-point exception does not occur. |
* The number is treated as 0 when the DN bit in the FPSW is 1. When the DN bit is 0, an unimplemented processing exception is generated. |
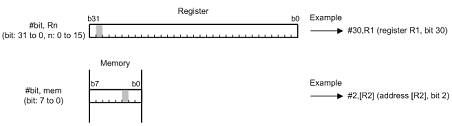
Five bit-manipulation instructions are provided for bitwise operations: BCLR, BMCnd, BNOT, BSET, and BTST.
A bit in a register is specified as the destination register and a bit number in the range from 31 to 0.
A bit in memory is specified as the destination address and a bit number from 7 to 0. The addressing modes available to specify addresses are register indirect and register relative.
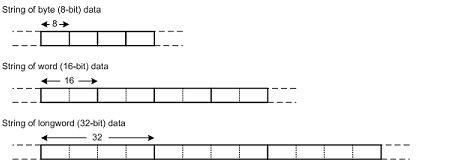
The string data type consists of an arbitrary number of consecutive byte (8-bit), word (16-bit), or longword (32-bit) units. Seven string manipulation instructions are provided for use with strings: SCMPU, SMOVB, SMOVF, SMOVU, SSTR, SUNTIL, and SWHILE.