Values of memory can be searched in the Memory Search dialog box that is opened by selecting [Find...] from the context menu. The search is operated either in the memory value area or character strings area, in which the caret exists. In this dialog box, follow the steps below.
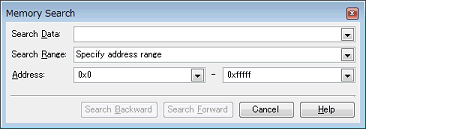
You can either type a value directly into the text box (up to 256 bytes), or select one from the input history via the drop-down list (up to 10 items).
If the search is performed in the memory value area, the value must be entered in the same display format (notation and size) as that area.
If the search is performed in the character strings area, then the target of the search must be a string. The specified string is converted into the encoding format displayed in that area, and searched for.
If a memory value was selected immediately prior to opening this dialog box, then that value will appear as default.
Select the range to search from the following drop-down list.
|
Searches in the address range specified in the [Address] area. |
|
|
Searches within the selected memory mapping range. This list item displays individual memory mapping configured in the Memory Mapping dialog box (except the non-mapped area). |
This item is only enabled if [Specify address range] is selected in the (2) Specify [Search Range].
Specify the range of memory address to search via the start and end addresses. You can either type address expressions directly into the text boxes (up to 1024 characters), or select them from the input history via the drop-down list (up to 10 items).
The results of calculating the address expressions you have entered are treated as start and end addresses, respectively.
Note that if an address value greater than the microcontroller address space is specified, the high-order address value is masked.
An address value greater than the value expressed within 32 bits cannot be specified.
A symbol name at the current caret position can be complemented by pressing the [Ctrl] + [Space] key in each text box (see "2.19.2 Symbol name completion function"). |
If the end address field is left blank, then it is treated as if the maximum value in the microcontroller's address space were specified. |
When the [Search Backward] button is clicked, search will start in the order from the large address number to small and the search results are displayed selected in the Memory panel.
When the [Search Forward] button is clicked, search will start in the order from the small address number to small and the search results are displayed selected in the Memory panel.