This option specifies the start address of the section.
Absolute address sections are allocated from smallest to largest, and then relative address sections starting at the end of the absolute address sections are allocated, in the order of appearance of the input files.
Wildcard characters (*, ?) can also be used for section. |
Two or more sections (specifying by delimiting them with a comma (,)) can be allocated to the same address (i.e., sections are overlaid) by delimiting them with a colon (:). |
Objects in a single section are allocated in the specified order of the input file and the input library. |
A section that is not specified by the -start option is allocated after the last allocation address. |
The example below shows how sections are allocated when the objects are input in the following order (The names enclosed by parentheses are sections in each object). |
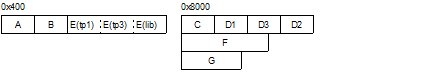
Sections specified with wildcard characters (in this example, the sections whose names start with "D") are allocated in the input order. |
Objects in the sections having the same name (section E in this example) are allocated in the input order. |
An input library's sections having the same name (section E in this example) are allocated after the input objects. |
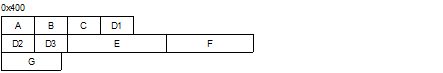
The sections that come immediately after ":" (sections A, D2, and G in this example) are selected as the start and allocated to the same address. |
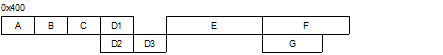
When the sections to be allocated to the same address are enclosed by "()", the sections within "()" are allocated to the address immediately after the sections that come before the "()" (sections C and E in this example). |
The section that comes after the "()" (section E in this example) is allocated after the last of the sections enclosed by "()". |
If the -form={object|relocate|library} option or -strip option is specified, this option will be invalid. |
One or more colons must be described within "()". |