6.3 Message Buffers
Multitask processing requires the inter-task communication function (message transfer function) that reports the processing result of a task to another task. The RI600V4 therefore provides the message buffers for copying and transferring the arbitrary size of message.
Message buffers therefore cannot be created dynamically using a method such as issuing a service call from a processing program.
Static message buffer creation means defining of message buffers using static API "message_buffer[]" in the system configuration file.
For details about the static API "message_buffer[]", refer to "19.13 Message Buffer Information (message_buffer[])".
- snd_mbf (Wait)
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
- There is a task in the reception wait queue.
This service call transfers the message specified by parameter msg to the task in the top of the reception wait queue. As a result, the task is unlinked from the reception wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message reception wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
This service call transfers the message specified by parameter msg to the task in the top of the reception wait queue. As a result, the task is unlinked from the reception wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message reception wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
- There is no task neither in the reception wait queue and transmission wait queue and there is available space in the message buffer.
This service call stores the message specified by parameter msg to the message buffer. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer decreases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
This service call stores the message specified by parameter msg to the message buffer. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer decreases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
- There is no task neither in the reception wait queue and transmission wait queue and there is no available space in the message buffer, or there is a task in the transmission wait queue.
This service call queues the invoking task to the transmission wait queue of the target message buffer and moves it from the RUNNING state to the WAITING state (message transmission wait state).
The sending WAITING state for a message buffer is cancelled in the following cases.
This service call queues the invoking task to the transmission wait queue of the target message buffer and moves it from the RUNNING state to the WAITING state (message transmission wait state).
The sending WAITING state for a message buffer is cancelled in the following cases.
#include "kernel.h" /*Standard header file definition*/ #include "kernel_id.h" /*Header file generated by cfg600*/ void task (VP_INT exinf) { ER ercd; /*Declares variable*/ ID mbfid = 1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ B msg[] = {1,2,3}; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ UINT msgsz = sizeof( msg ); /*Declares and initializes variable*/ /* ......... */ ercd = snd_mbf (mbfid, (VP)msg, msgsz); /*Send to message buffer*/ if (ercd == E_OK) { /* ......... */ /*Normal termination processing*/ } else if (ercd == E_RLWAI) { /* ......... */ /*Forced termination processing*/ } /* ......... */ } |
Note 1 Message is written to the message buffer area in the order of the message transmission request.
Note 2 Invoking tasks are queued to the transmission wait queue of the target message buffer in the FIFO order.
- psnd_mbf, ipsnd_mbf (Polling)
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
- There is a task in the reception wait queue.
This service call transfers the message specified by parameter msg to the task in the top of the reception wait queue. As a result, the task is unlinked from the reception wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message reception wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
This service call transfers the message specified by parameter msg to the task in the top of the reception wait queue. As a result, the task is unlinked from the reception wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message reception wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
- There is no task neither in the reception wait queue and transmission wait queue and there is available space in the message buffer.
This service call stores the message specified by parameter msg to the message buffer. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer decreases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
This service call stores the message specified by parameter msg to the message buffer. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer decreases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
- There is no task neither in the reception wait queue and transmission wait queue and there is no available space in the message buffer, or there is a task in the transmission wait queue.
This service call returns "E_TMOUT".
This service call returns "E_TMOUT".
#include "kernel.h" /*Standard header file definition*/ #include "kernel_id.h" /*Header file generated by cfg600*/ void task (VP_INT exinf) { ER ercd; /*Declares variable*/ ID mbfid = 1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ B msg[] = {1,2,3}; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ UINT msgsz = sizeof( msg ); /*Declares and initializes variable*/ /* ......... */ ercd = psnd_mbf (mbfid, (VP)msg, msgsz); /*Send to message buffer*/ if (ercd == E_OK) { /* ......... */ /*Polling success processing*/ } else if (ercd == E_TMOUT) { /* ......... */ /*Polling failure processing*/ } /* ......... */ } |
Note Message is written to the message buffer area in the order of the message transmission request.
- tsnd_mbf (Wait with time-out)
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
- There is a task in the reception wait queue.
This service call transfers the message specified by parameter msg to the task in the top of the reception wait queue. As a result, the task is unlinked from the reception wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message reception wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
This service call transfers the message specified by parameter msg to the task in the top of the reception wait queue. As a result, the task is unlinked from the reception wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message reception wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
- There is no task neither in the reception wait queue and transmission wait queue and there is available space in the message buffer.
This service call stores the message specified by parameter msg to the message buffer. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer decreases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
This service call stores the message specified by parameter msg to the message buffer. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer decreases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
- There is no task neither in the reception wait queue and transmission wait queue and there is no available space in the message buffer, or there is a task in the transmission wait queue.
This service call queues the invoking task to the transmission wait queue of the target message buffer and moves it from the RUNNING state to the WAITING state with time (message transmission wait state).
The sending WAITING state for a message buffer is cancelled in the following cases.
This service call queues the invoking task to the transmission wait queue of the target message buffer and moves it from the RUNNING state to the WAITING state with time (message transmission wait state).
The sending WAITING state for a message buffer is cancelled in the following cases.
#include "kernel.h" /*Standard header file definition*/ #include "kernel_id.h" /*Header file generated by cfg600*/ void task (VP_INT exinf) { ER ercd; /*Declares variable*/ ID mbfid = 1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ B msg[] = {1,2,3}; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ TMO tmout = 3600; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ /* ......... */ ercd = tsnd_mbf (mbfid, (VP)msg, msgsz, tmout); /*Send to message buffer*/ if (ercd == E_OK) { /* ......... */ /*Normal termination processing*/ } else if (ercd == E_RLWAI) { /* ......... */ /*Forced termination processing*/ } else if (ercd == E_TMOUT) { /* ......... */ /*Time-out processing*/ } /* ......... */ } |
Note 1 Message is written to the message buffer area in the order of the message transmission request.
Note 2 Invoking tasks are queued to the transmission wait queue of the target message buffer in the FIFO order.
Note 3 TMO_FEVR is specified for wait time tmout, processing equivalent to snd_mbf will be executed. When TMO_POL is specified, processing equivalent to psnd_mbf will be executed.
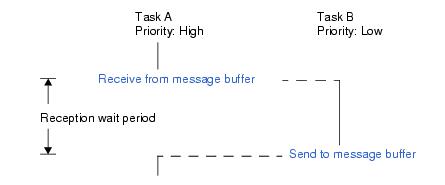
A message is received (waiting forever, polling, or with time-out) by issuing the following service call from the processing program.
- rcv_mbf (Wait)
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
- There is a message in the message buffer.
This service call takes out the oldest message from the message buffer and stores the message to the area specified by msg and return the size of the message. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer increases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
This service call takes out the oldest message from the message buffer and stores the message to the area specified by msg and return the size of the message. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer increases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
In addition, this service call repeats the following processing until task in the transmission wait queue is lost or it becomes impossible to store the message in the message buffer.
- When there is a task in the transmission wait queue and there is available space in the message buffer for the message specified by the task in the top of the transmission wait queue, the task is unlinked from the transmission wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message transmission wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer decreases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
- There is no message in the message buffer and there is a task in the transmission wait queue.
This service call stores the message specified by the task in the top of the transmission wait queue to the area pointed by the parameter msg. As a result, the task is unlinked from the transmission wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message transmission wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
Note, this situation is caused only when the size of the message buffer is 0.
This service call stores the message specified by the task in the top of the transmission wait queue to the area pointed by the parameter msg. As a result, the task is unlinked from the transmission wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message transmission wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
Note, this situation is caused only when the size of the message buffer is 0.
- There is no message in the message buffer and there is no task in the transmission wait queue.
This service call queues the invoking task to the reception wait queue of the target message buffer and moves it from the RUNNING state to the WAITING state (message reception wait state).
The receiving WAITING state for a message buffer is cancelled in the following cases.
This service call queues the invoking task to the reception wait queue of the target message buffer and moves it from the RUNNING state to the WAITING state (message reception wait state).
The receiving WAITING state for a message buffer is cancelled in the following cases.
#include "kernel.h" /*Standard header file definition*/ #include "kernel_id.h" /*Header file generated by cfg600*/ void task (VP_INT exinf) { ER ercd; /*Declares variable*/ ID mbfid = 1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ B msg[16]; /*Declares variable (maximum message size)*/ /* ......... */ ercd = rcv_mbf (mbfid, (VP)msg); /*Receive from message buffer */ if (ercd == E_OK) { /* ......... */ /*Normal termination processing*/ } else if (ercd == E_RLWAI) { /* ......... */ /*Forced termination processing*/ } /* ......... */ } |
Note 1 The Maximum message size (max_msgsz) is defined during configuration. The size of the area pointed by msg must be larger than or equal to the maximum message size.
Note 2 Invoking tasks are queued to the reception wait queue of the target message buffer in the order of the message reception request.
- prcv_mbf (Polling)
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
- There is a message in the message buffer.
This service call takes out the oldest message from the message buffer and stores the message to the area specified by msg and return the size of the message. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer increases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
This service call takes out the oldest message from the message buffer and stores the message to the area specified by msg and return the size of the message. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer increases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
In addition, this service call repeats the following processing until task in the transmission wait queue is lost or it becomes impossible to store the message in the message buffer.
- When there is a task in the transmission wait queue and there is available space in the message buffer for the message specified by the task in the top of the transmission wait queue, the task is unlinked from the transmission wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message transmission wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer decreases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
- There is no message in the message buffer and there is a task in the transmission wait queue.
This service call stores the message specified by the task in the top of the transmission wait queue to the area pointed by the parameter msg. As a result, the task is unlinked from the transmission wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message transmission wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
Note, this situation is caused only when the size of the message buffer is 0.
This service call stores the message specified by the task in the top of the transmission wait queue to the area pointed by the parameter msg. As a result, the task is unlinked from the transmission wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message transmission wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
Note, this situation is caused only when the size of the message buffer is 0.
- There is no message in the message buffer and there is no task in the transmission wait queue.
This service call returns "E_TMOUT".
This service call returns "E_TMOUT".
#include "kernel.h" /*Standard header file definition*/ #include "kernel_id.h" /*Header file generated by cfg600*/ void task (VP_INT exinf) { ER ercd; /*Declares variable*/ ID mbfid = 1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ B msg[16]; /*Declares variable (maximum message size)*/ /* ......... */ ercd = prcv_mbf (mbfid, (VP)msg); /*Receive from message buffer */ if (ercd == E_OK) { /* ......... */ /*Polling success processing*/ } else if (ercd == E_TMOUT) { /* ......... */ /*Polling failure processing*/ } /* ......... */ } |
Note The Maximum message size (max_msgsz) is defined during configuration. The size of the area pointed by msg must be larger than or equal to the maximum message size.
- trcv_mbf (Wait with time-out)
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
This service call processes as follows according to the situation of the message buffer specified by the parameter mbfid.
- There is a message in the message buffer.
This service call takes out the oldest message from the message buffer and stores the message to the area specified by msg and return the size of the message. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer increases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
This service call takes out the oldest message from the message buffer and stores the message to the area specified by msg and return the size of the message. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer increases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
In addition, this service call repeats the following processing until task in the transmission wait queue is lost or it becomes impossible to store the message in the message buffer.
- When there is a task in the transmission wait queue and there is available space in the message buffer for the message specified by the task in the top of the transmission wait queue, the task is unlinked from the transmission wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message transmission wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state. As a result, the size of available space in the target message buffer decreases by the amount calculated by the following expression.
- There is no message in the message buffer and there is a task in the transmission wait queue.
This service call stores the message specified by the task in the top of the transmission wait queue to the area pointed by the parameter msg. As a result, the task is unlinked from the transmission wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message transmission wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
Note, this situation is caused only when the size of the message buffer is 0.
This service call stores the message specified by the task in the top of the transmission wait queue to the area pointed by the parameter msg. As a result, the task is unlinked from the transmission wait queue and moves from the WAITING state (message transmission wait state) to the READY state, or from the WAITING-SUSPENDED state to the SUSPENDED state.
Note, this situation is caused only when the size of the message buffer is 0.
- There is no message in the message buffer and there is no task in the transmission wait queue.
This service call queues the invoking task to the reception wait queue of the target message buffer and moves it from the RUNNING state to the WAITING state with time (message reception wait state).
The receiving WAITING state for a message buffer is cancelled in the following cases.
This service call queues the invoking task to the reception wait queue of the target message buffer and moves it from the RUNNING state to the WAITING state with time (message reception wait state).
The receiving WAITING state for a message buffer is cancelled in the following cases.
#include "kernel.h" /*Standard header file definition*/ #include "kernel_id.h" /*Header file generated by cfg600*/ void task (VP_INT exinf) { ER ercd; /*Declares variable*/ ID mbfid = 1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ B msg[16]; /*Declares variable (maximum message size)*/ TMO tmout = 3600; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ /* ......... */ ercd = trcv_mbf (mbfid, (VP)msg, tmout ); /*Receive from message buffer */ if (ercd == E_OK) { /* ......... */ /*Normal termination processing*/ } else if (ercd == E_RLWAI) { /* ......... */ /*Forced termination processing*/ } else if (ercd == E_TMOUT) { /* ......... */ /*Time-out processing*/ } /* ......... */ } |
Note 1 The Maximum message size (max_msgsz) is defined during configuration. The size of the area pointed by msg must be larger than or equal to the maximum message size.
Note 2 Invoking tasks are queued to the reception wait queue of the target message buffer in the order of the message reception request.
Note 3 TMO_FEVR is specified for wait time tmout, processing equivalent to rcv_mbf will be executed. When TMO_POL is specified, processing equivalent to prcv_mbf will be executed.
A message buffer status is referenced by issuing the following service call from the processing program.
- ref_mbf, iref_mbf
These service calls store the detailed information of the message buffer (existence of waiting tasks, available buffer size, etc.) specified by parameter mbfid into the area specified by parameter pk_rmbf.
The following describes an example for coding this service call.
These service calls store the detailed information of the message buffer (existence of waiting tasks, available buffer size, etc.) specified by parameter mbfid into the area specified by parameter pk_rmbf.
The following describes an example for coding this service call.
#include "kernel.h" /*Standard header file definition*/ #include "kernel_id.h" /*Header file generated by cfg600*/ void task (VP_INT exinf) { ID mbfid = 1; /*Declares and initializes variable*/ T_RMBF pk_rmbf; /*Declares message structure*/ ID stskid; /*Declares variable*/ ID rtskid; /*Declares variable*/ UINT smsgcnt; /*Declares variable*/ SIZE fmbfsz; /*Declares variable*/ /* ......... */ ref_mbf (mbfid, &pk_rmbf); /*Reference message buffer state*/ stskid = pk_rmbf.stskid; /*Acquires existence of tasks waiting for */ /*message transmission*/ rtskid = pk_rmbf.rtskid; /*Acquires existence of tasks waiting for */ /*message reception*/ smsgcnt = pk_rmbf.smsgcnt; /*Acquires the number of message in */ /*message buffer*/ fmbfsz = pk_rmbf.fmbfsz; /*Acquires the available buffer size */ /* ......... */ } |
Note For details about the message buffer state packet, refer to "[Message buffer state packet: T_RMBF]".