In the [Connect Settings] tab, you configure the connection with the debug tool for each one of the following categories.
(3) [Connection with Emulator]
(4) [Connection with Target Board]
(5) [E2 Expansion Interface] [E2]
The configuration of internal ROM/RAM is displayed in this category.
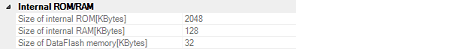
The internal ROM size to emulate is displayed (unit: Kbytes).
You cannot change the value of this property.
The internal RAM size to emulate is displayed (unit: bytes).
You cannot change the value of this property.
The data flash memory size is displayed (unit: Kbytes).
If the currently selected microcontroller does not incorporate the data flash, [0] is displayed.
You cannot change the value of this property.
You can configure the clock in this category.
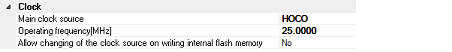
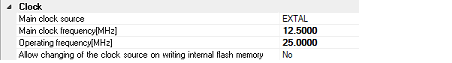
Select EXTAL frequency or internal HOCO as the main clock source. [EXTAL] will be displayed for microcontrollers with no internal HOCO.
Specify the main clock frequency (before multiplier).
Specify EXTAL frequency by directly entering a number between 0.0001 and 99.9999 (MHz). The entered value will be truncated to 4 decimal places. If the value is out of the specifiable range, it will be rounded to 0.0001 (when 0 or below) or to 99.9999 (when 100 or above).
This property is displayed only when you have selected [EXTAL] in the [Main clock source] property.
Specify the Operating frequency (ICLK) by directly entering a number between 0.0001 and 999.9999 (MHz).
If you enter a value with more than four decimal places, the entered value will be truncated to four decimal places. If the value is out of the specifiable range, it will be rounded to 0.0001 (if 0 or negative) or to 999.9999 (if 1000 or greater).
Specify whether to allow a debugger to operate the clock while the internal flash memory is being rewritten.
You can configure the connection between E1 and the host machine in this category.
Serial numbers of all connected E1 emulators are displayed in the drop-down list.
Select the one to be connected to the target system.
The drop-down list is updated every time it is used.
You can configure the connection between E1 and the target board in this category.
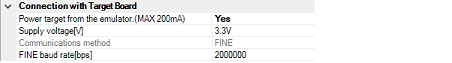
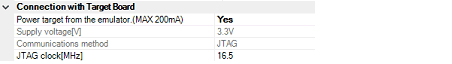
Specify whether to supply power to the target system from E1.
Select [Yes] to supply power to the target system ([No] is selected by default).
This property appears only when the [Power target from the emulator. (MAX 200mA)] property is set to [Yes].
Select the interface for supplying the power to the target board from the emulator (default: [USER I/F]).
Specify the power voltage supplied to the target system from the following drop-down list.
This property appears only when the [Power target from the emulator. (MAX 200mA)] property is set to [Yes].
The voltage value that can be specified differs depending on the type of the microcontroller.
This property cannot be changed.
Displays the method of communication used by the E1 emulator for communicating with the microcontroller on the target system. Specifying [RX E1(Serial)] for a debug tool in the Project Tree panel will display [FINE] in this property, and specifying [RX E1(JTAG)] will display [JTAG].
You cannot change the value of this property when specifying E1. When specifying [RX E2 Lite] or [RX E2], whether this property can be changed differs with the type of the selected microcontroller and the communication method. See "2.2.1 Confirm the connection to a host machine" for the relationship between types of the microcontroller and the communication method.
For the details of debug tool selection, see "2.3.1 Select the debug tool to use".
From the drop-down list, select the baud rate (JTAG clock) to be used by the E1 emulator for communicating with the microcontroller on the target system.
This property is displayed only when [JTAG] is selected in the [Communications method] property.
The following baud rate is displayed in the drop-down list.
Depending on the length or the method of JTAG signal wiring on the target system, it may not be possible to communicate using the selected JTAG clock. In such a case, reducing the JTAG clock may achieve successful communication. |
From the drop-down list, select the baud rate (FINE baud rate) to be used by the E1 emulator for communicating with the microcontroller on the target system.
This property is displayed only when [FINE] is selected in the [Communications method] property.
The following baud rate is displayed in the drop-down list.
Depending on the length or the method of FINE signal wiring on the target system, it may not be possible to communicate using the selected FINE baud rate. In such a case, reducing the FINE baud rate achieve successful communication. |
You can configure the E2 expansion interface.

Select whether to use the E2 expansion interface.
If you want to use the E2 expansion interface, select the power used by the E2 expansion interface.
You can configure the flash memory rewriting in this category.
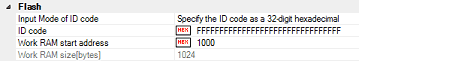
Specify a mode for the input of ID code.
Enter the ID code to release the flash memory from the protected state.
If you have selected [Specify the ID code as a 32-digit hexadecimal] in the [Input Mode of ID code] property, enter the ID code in a 32-digit hexadecimal number. If you have selected [Specify the ID code as an ASCII code within 16 characters], enter the ID code using maximum 16 ASCII characters.
To enter the ID code as a 32-digit hexadecimal value, arrange it as a sequence of 32-bit units of data. |
If the ID code entered in ASCII characters is shorter than 16 characters, the unused space will be padded with 0. |
Even if you have downloaded a program that contains an ID code, that ID code is replaced with FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF. |
Specify the location address of the work RAM to be used by the debugger. Specify an address value that is a multiple of four bytes. If the entered value is not a multiple of four bytes, the value is automatically corrected.
The amount of memory indicated by the [Work RAM size[bytes] property beginning with this address is to be used by the debugger firmware.
The work RAM area can also be used by the user program because the emulator saves and restores data in this area. Note, however, that the work RAM area is not specifiable as: |
Displays the size of the work RAM to be used by the debugger.
In this category, you configure the operating mode of the microcontroller to be emulated.
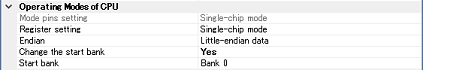
Specify the operating mode set by the mode pin of the microcontroller.
Select whether to erase the USB boot program in the user boot area when you are starting up the emulator in the user boot mode by using a microcontroller in which the USB boot program is stored.
This property is displayed only when [User boot mode] is selected for the [Mode pins setting] property.
Note that this is not displayed for an microcontroller in which the USB boot program in the user boot area does not need to be erased when you are starting up the emulator.
Specify the operating mode to be set by the register.
The operating mode that can be specified depends on the type of the microcontroller.
Display the project endian. Acquires endian information from the project and displays its value. Can be selected only when the debug tool is disconnected.
Specify whether to change the start bank before connecting to the debug tool.
Select [Yes] to change the start bank before connecting to the debug tool ([No] is selected by default).
Specify the start bank to be changed before connecting to the debug tool.
This property is displayed only when [Yes] is selected for the [Change the start bank][RX651-2M and RX65N-2M Groups] property.
In this category, you can configure external flash.
The settings in this category are required when downloading to an external flash memory. For more details regarding property setting, see "2.5.2.5 Downloading files to external flash memory [E1] [E20]“.