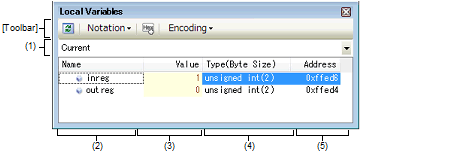
This panel is used to display the contents of the local variable and change the local variable values (see "2.10.5 Display/change local variables").
This panel appears only when connected to the debug tool.
Nothing is displayed on this panel during execution of a program. When the execution of a program is stopped, items in each area are displayed. |
Because of optimization by a compiler, for blocks where variables, or the subject to be operated on, are not in use, there may be no variable data in the stack and registers. In this case, no variables are displayed that are the subject to be operated on. |
This panel can be zoomed in and out by |
When the separator line of each area in this panel is double-clicked, the width of the area changes to the shortest possible size that can display the contents of the area. |
This section describes the following.
Select the scope of the local variable to be displayed from the following drop-down list.
The calling functions displayed on theCall Stack panel are displayed. |
When scope information that has lost its reliability, items in the list is shown in gray (the character color/background color when showing "Invalid" depends on the configuration in the [General - Font and Color] category of the Option dialog box). |
The local variable name or function name is displayed.
The argument of the function is also displayed as the local variable.
In addition, the hierarchical structure is displayed in tree format for arrays, pointer variables, and structures/unions/class.
The meanings of the icons are as follows:
When Auto variables are used to display local variables, accurate values cannot be displayed at a prologue ("{") or epilogue ("}") of a function. The Auto variable addresses are the relative addresses from the address pointed to by the stack pointer (SP), so their addresses are not determined until the SP value is determined in the function. The SP is manipulated via prologues or epilogues, so the accurate value cannot be displayed. |
This area is provided with the following functions.
Variable names of C language can be registered in the Watch panel as watch-expressions.
See "2.10.6.1 Register a watch-expression" for details on how to operate it.
By selecting [Jump to Memory] from the context menu, the Memory panel (Memory1) opens with moving the caret to the source line corresponding to the address where the selected local variable is disposed (if the Memory panel (Memory1) is already open, the screen will jump to the panel).
The value of the local variable is displayed and changed.
The notation of a data value can be selected by the button on the toolbar or the context menu item. In addition, a display format adding the value in hexadecimal number constantly can also be selected as well.
The meanings of the marks and colors displayed as the values of the local variables are as follows (character colors and background colors depend on the configuration in the [General - Font and Color] category of the Option dialog box):
Variables that the name stays same from the start point where the program started executing to the breakpoint and their values are changed are the target. |
This area is provided with the following functions.
To edit the local variable value or the argument value, select the value to edit, then change the value directly from the keyboard after clicking again on it (press the [Esc] key to cancel the edit mode).
After you edit the value of the local variable or the argument, it is written to the target memory of the debug tool by pressing the [Enter] key or moving the focus to outside the edit region.
See "2.10.5.2 Modify the contents of local variables" for details on the method for changing the local variable/argument value.
The Save As dialog box can be opened by selecting the [File] menu >> [Save Local Variables Data As...], and all the contents of this panel can be saved in a text file (*.txt) or CSV file (*.csv).
See "2.10.5.3 Save the contents of local variables" for details on the method for saving the contents of the local variable.
The type name of the local variable is displayed. The notation accords with the description of C language.
For an array, an element number is displayed in "[]". For a function, its size (number of bytes) is displayed in "()".
The address of the local variable is displayed. When a variable is assigned to the register, the name of the register is displayed.
These buttons below are disabled during execution of a program.
[[File] menu (Local Variables panel-dedicated items)]
The following items are exclusive for the [File] menu in the Local Variables panel (other items are common to all the panels).
Note that all these items are disabled during execution of a program.
|
Overwrites the contents of this panel to the previously saved text file (*.txt)/CSV file (*.csv) (see "(b) Saving the contents of the local variable"). Note that when the file has never been saved or the file is write disabled, the same operation is applied as the selection in [Save Local Variables Data As...]. |
|
|
Opens the Save As dialog box to newly save the contents of this panel to the specified text file (*.txt)/CSV file (*.csv) (see "(b) Saving the contents of the local variable"). |
[[Edit] menu (Local Variables panel-dedicated items)]
The following items are exclusive for [Edit] menu in the Local Variables panel (all other items are disabled).
|
Copies the contents of the selected line or the character string to the clipboard. |
|
|
Changes to the edit mode to edit the selected local variable value (see "2.10.5.2 Modify the contents of local variables"). |
|
|
Opens the Find and Replace dialog box with selecting the [Find in Files] tab. |
|
|
Opens the Find and Replace dialog box with selecting the [Replace in Files] tab. |
|
Registers the selected local variable to the Watch panel (Watch1). |
||
|
Copies the contents of the selected line or the character string to the clipboard. |
||
|
The following cascade menus to specify the notation of values are displayed. |
||
|
Displays values on this panel in the default notation according to the type of variable (default). |
||
|
Displays array indexes on this panel in decimal number (default). |
||
|
Displays values on this panel in Float. Note that when the value is not 4-byte data, or has the type information, displays it in the default notation. |
||
|
Displays values on this panel in Double. Note that when the value is not 4-byte data, or has the type information, displays it in the default notation. |
||
|
Adds the value in hexadecimal number enclosing with "()" at the end of the value. |
||
|
The following cascade menus to specify the encoding of character variables are displayed. |
||
|
Opens the Memory panel (Memory1) and jumps to the memory value corresponding to the address of the selected line in this panel. |
||
 in the tool bar, or by moving the mouse wheel forward or backward while holding down the [Ctrl] key.
in the tool bar, or by moving the mouse wheel forward or backward while holding down the [Ctrl] key.


 AutoSelect
AutoSelect Hexadecimal
Hexadecimal Decimal
Decimal Octal
Octal Binary
Binary Decimal Notation for Array Index
Decimal Notation for Array Index Hexadecimal Notation for Array Index
Hexadecimal Notation for Array Index Float
Float Double
Double
 ASCII
ASCII Shift_JIS
Shift_JIS EUC-JP
EUC-JP UTF-8
UTF-8 UTF-16 Big-Endian
UTF-16 Big-Endian UTF-16 Little-Endian
UTF-16 Little-Endian UTF-32 Big-Endian
UTF-32 Big-Endian UTF-32 Little-Endian
UTF-32 Little-Endian