CHAPTER 16 SYSTEM INITIALIZATION
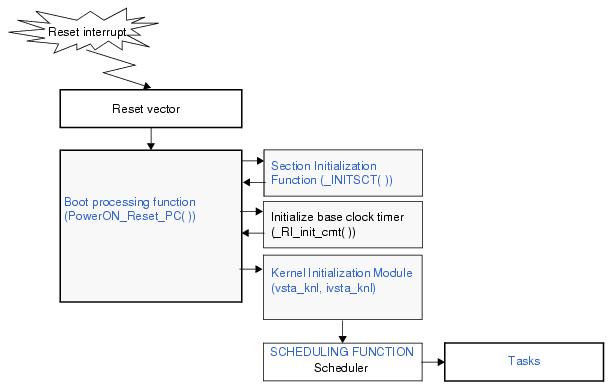
The following shows a processing flow from when a reset interrupt occurs until the control is passed to the task.
2 ) System down routine (_RI_sys_dwn__)
For details, refer to "13.2.1 System down routine (_RI_sys_dwn__)".
For details, refer to "13.2.1 System down routine (_RI_sys_dwn__)".
Note The boot processing file which is provided by the RI600V4 as a sample file is resetprg.c. This file includes System down routine (_RI_sys_dwn__).
The boot processing function is the program registered in the reset vector, and is executed in supervisor mode. Generally, following processing are required in the boot processing function.
- Initialize the processor and hardwares
If using Fast Interrupt of the RX-MCU, initialize the FINTV register to the start address of the fast interrupt handler.
If using Fast Interrupt of the RX-MCU, initialize the FINTV register to the start address of the fast interrupt handler.
- Initialize base clock timer
Call "void _RI_init_cmt(void)" which is defined in the "ri_cmt.h" generated by the cfg600.
Refer to "8.9 Initialize Base Clock Timer".
Call "void _RI_init_cmt(void)" which is defined in the "ri_cmt.h" generated by the cfg600.
Refer to "8.9 Initialize Base Clock Timer".
- Basic form of boot processing function
The boot processing function should be implemented as "void PowerON_Reset_PC(void)". When the name of the boot processing function is other, it is necessary to define the function name to "interrupt_fvector[31]" in the system configuration file.
The boot processing function should be implemented as "void PowerON_Reset_PC(void)". When the name of the boot processing function is other, it is necessary to define the function name to "interrupt_fvector[31]" in the system configuration file.
Note For the details of the details of the static API "interrupt_fvector[]", refer to "19.19 Fixed Vector/Exception Vector Information (interrupt_fvector[])".
- Stack
Describe #pragma entry directive to be shown below. Thereby, the object code which sets the stack pointer (ISP) as the system stack at the head of the boot processing function is generated.
Describe #pragma entry directive to be shown below. Thereby, the object code which sets the stack pointer (ISP) as the system stack at the head of the boot processing function is generated.
- PSW register
Keep the status that all interrupts are prohibited and in the supervisor mode until calling the Kernel Initialization Module (vsta_knl, ivsta_knl). This status is satisfied just behind CPU reset (PSW.I=0, PSW.PM=0). Generally, the boot processing function should not change the PSW.
Keep the status that all interrupts are prohibited and in the supervisor mode until calling the Kernel Initialization Module (vsta_knl, ivsta_knl). This status is satisfied just behind CPU reset (PSW.I=0, PSW.PM=0). Generally, the boot processing function should not change the PSW.
- EXTB register (RXv2 architecture)
Initialize EXTB register to the start address of FIX_INTERRUPT_VECTOR section if needed. Please refer to "FIX_INTERRUPT_VECTOR section" in section 2.6.4.
Initialize EXTB register to the start address of FIX_INTERRUPT_VECTOR section if needed. Please refer to "FIX_INTERRUPT_VECTOR section" in section 2.6.4.
- Service call
Since the boot processing function is executed before executing of Kernel Initialization Module (vsta_knl, ivsta_knl), service calls except vsta_knl and ivsta_knl must not be called from the boot processing function.
Since the boot processing function is executed before executing of Kernel Initialization Module (vsta_knl, ivsta_knl), service calls except vsta_knl and ivsta_knl must not be called from the boot processing function.
The boot processing file must include "kernel_ram.h" and "kernel_rom.h", which are generated by the cfg600, in this order.
The kernel initialization module is executed by calling vsta_knl, ivsta_knl. Generally, vsta_knl, ivsta_knl is called from the Boot processing function (PowerON_Reset_PC( )).
2 ) Initialize INTB register to the start address of the relocatable vector table (INTERRUPT_VECTOR section). The relocatable vector table is generated by the cfg600.
The section initialization function "_INITSCT()" called from Boot processing function (PowerON_Reset_PC( )) is provided by the compiler. The _INITSCT() clears the uninitialized data section to 0 and initializes the initialized data section in order to the tables described in the Section information file (User-Own Coding Module).
The user needs to write the sections to be initialized to the tables for section initialization (DTBL and BTBL) in the section information file. The section address operator is used to set the start and end addresses of the sections used by the _INITSCT(). Section names in the section initialization tables are declared, using C$BSEC for uninitialized data areas, and
Initialized sections written in DTBL must be mapped from ROM to RAM by using "-rom" linker option. For details, refer to "2.6.5 Initialized data section".
For some MCUs, the endian select register, ID code protection on connection of the on-chip debugger, etc. are assigned in the address from 0xFFFFFF80 to 0xFFFFFFBF in fixed vector table (RXv1 architecture) / exception vector table (RXv2 architecture). To set up such registers, describe "interrupt_fvector[]" in the system configuration file. For details, refer to "19.19 Fixed Vector/Exception Vector Information (interrupt_fvector[])".