|
|
|
|
|
Constant
(macro)
|
EDOM
|
Indicates the value to be set in errno if the value of a parameter input to a function is outside the range of values defined in the function.
|
|
ERANGE
|
Indicates the value to be set in errno if the result of a function cannot be represented as a double type value, or if an overflow or an underflow occurs.
|
|
HUGE_VAL
HUGE_VALF <-lang=c99>
HUGE_VALL <-lang=c99>
|
Indicates the value for the function return value if the result of a function overflows.
|
|
INFINITY <-lang=c99>
|
Expanded to a float-type constant expression that represents positive or unsigned infinity.
|
|
NAN <-lang=c99>
|
Defined when float-type qNaN is supported.
|
|
FP_INFINITE <-lang=c99>
FP_NAN <-lang=c99>
FP_NORMAL <-lang=c99>
FP_SUBNORMAL <-lang=c99>
FP_ZERO <-lang=c99>
|
These indicate exclusive types of floating-point values.
|
|
FP_ILOGB0 <-lang=c99>
FP_ILOGBNAN <-lang=c99>
|
These are expanded to an integer constant expression of the value returned by ilogb when they are 0 or not-a-number, respectively.
|
|
MATH_ERRNO <-lang=c99>
MATH_ERREXCEPT <-lang=c99>
|
These are expanded to integer constants 1 and 2, respectively.
|
|
math_errhandling <-lang=c99>
|
Expanded to an int-type expression whose value is a bitwise logical OR of MATH_ERRNO and MATH_ERREXCEPT.
|
|
Type
|
float_t <-lang=c99>
double_t <-lang=c99>
|
These are floating-point types having the same width as float and double, respectively.
|
|
Function (macro)
|
fpclassify <-lang=c99>
|
Classifies argument values into not-a-number, infinity, normalized number, denormalized number, and 0.
|
|
isfinite <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the argument is a finite value.
|
|
isinf <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the argument is infinity.
|
|
isnan <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the argument is a not-a-number.
|
|
isnormal <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the argument is a normalized number.
|
|
signbit <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the sign of the argument is negative.
|
|
isgreater <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the first argument is greater than the second argument.
|
|
isgreaterequal <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the first argument is equal to or greater than the second argument.
|
|
isless <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the first argument is smaller than the second argument.
|
|
islessequal <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the first argument is equal to or smaller than the second argument.
|
|
islessgreater <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the first argument is smaller or greater than the second argument.
|
|
isunordered <-lang=c99>
|
Determines whether the arguments are not ordered.
|
|
Function
|
acos / acosf / acosl
|
Calculates the arc cosine of a floating-point number.
|
|
asin / asinf / asinl
|
Calculates the arc sine of a floating-point number.
|
|
atan / atanf / atanl
|
Calculates the arc tangent of a floating-point number.
|
|
atan2 / atan2f / atan2l
|
Calculates the arc tangent of the result of a division of two floating-point numbers.
|
|
cos / cosf / cosl
|
Calculates the cosine of a floating-point radian value.
|
|
sin / sinf / sinl
|
Calculates the sine of a floating-point radian value.
|
|
tan / tanf / tanl
|
Calculates the tangent of a floating-point radian value.
|
|
cosh / coshf / coshl
|
Calculates the hyperbolic cosine of a floating-point number.
|
|
sinh / sinhf / sinhl
|
Calculates the hyperbolic sine of a floating-point number.
|
|
tanh / tanhf / tanhl
|
Calculates the hyperbolic tangent of a floating-point number.
|
|
exp / expf / expl
|
Calculates the exponential function of a floating-point number.
|
|
frexp / frexpf / frexpl
|
Breaks a floating-point number into a [0.5, 1.0) value and a power of 2.
|
|
ldexp / ldexpf / ldexpl
|
Multiplies a floating-point number by a power of 2.
|
|
log / logf / logl
|
Calculates the natural logarithm of a floating-point number.
|
|
log10 / log10f / log10l
|
Calculates the base-ten logarithm of a floating-point number.
|
|
modf / modff / modfl
|
Breaks a floating-point number into integral and fractional parts.
|
|
pow / powf / powl
|
Calculates a power of a floating-point number.
|
|
sqrt / sqrtf / sqrtl
|
Calculates the positive square root of a floating-point number.
|
|
Function
|
ceil / ceilf / ceill
|
Calculates the smallest integral value not less than or equal to the given floating-point number.
|
|
fabs / fabsf / fabsl
|
Calculates the absolute value of a floating-point number.
|
|
floor / floorf / floorl
|
Calculates the largest integral value not greater than or equal to the given floating-point number.
|
|
fmod / fmodf / fmodl
|
Calculates the remainder of a division of two floating-point numbers.
|
|
acosh / acoshf / acoshl
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the hyperbolic arc cosine of a floating-point number.
|
|
asinh / asinhf / asinhl
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the hyperbolic arc sine of a floating-point number.
|
|
atanh / atanhf / atanhl
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the hyperbolic arc tangent of a floating-point number.
|
|
exp2 / exp2f / exp2l
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the value of 2 raised to the power x.
|
|
expm1 / expm1f / expm1l
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the natural logarithm raised to the power x and subtracts 1 from the result.
|
|
ilogb / ilogbf / ilogbl
<-lang=c99>
|
Extracts the exponent of x as a signed int value.
|
|
log1p / log1pf / log1pl
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the natural logarithm of the argument + 1.
|
|
log2 / log2f / log2l
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the base-2 logarithm.
|
|
logb / logbf / logbl
<-lang=c99>
|
Extracts the exponent of x as a signed integer.
|
|
scalbn / scalbnf / scalbnl / scalbln / scalblnf / scalblnl
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates x × FLT_RADIXn.
|
|
cbrt / cbrtf / cbrtl
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the cube root of a floating-point number.
|
|
hypot / hypotf / hypotl
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the square root of the sum of squares of two
parameters (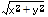 ).
).
|
|
erf / erff / erfl
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the error function.
|
|
erfc / erfcf / erfcl
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the complementary error function.
|
|
lgamma / lgammaf / lgammal
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the natural logarithm of the absolute value of the gamma function.
|
|
tgamma / tgammaf / tgammal
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the gamma function.
|
|
nearbyint / nearbyintf / nearbyintl
<-lang=c99>
|
Rounds a floating-point number to an integer in the floating-point representation according to the current rounding direction.
|
|
rint / rintf / rintl
<-lang=c99>
|
Equivalent to nearbyint except that this function group may generate floating-point exception.
|
|
Function
|
lrint / lrintf / lrintl / llrint / llrintf / llrintl
<-lang=c99>
|
Rounds a floating-point number to the nearest integer according to the rounding direction.
|
|
round / roundf / roundl
<-lang=c99>
|
Rounds a floating-point number to the nearest integer in the floating-point representation.
|
|
lround / lroundf / lroundl / llround / llroundf / llroundl
<-lang=c99>
|
Rounds a floating-point number to the nearest integer.
|
|
trunc / truncf / truncl
<-lang=c99>
|
Rounds a floating-point number to the nearest integer in the floating-point representation.
|
|
remainder / remainderf / remainderl
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates remainder x REM y specified in the IEEE60559 standard.
|
|
remquo / remquof / remquol
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the value having the same sign as x/y and the absolute value congruent modulo-2n to the absolute value of the quotient.
|
|
copysign / copysignf / copysignl
<-lang=c99>
|
Generates a value consisting of the given absolute value and sign.
|
|
nan / nanf / nanl
<-lang=c99>
|
nan("n string") is equivalent to ("NAN(n string)", (char**) NULL).
|
|
nextafter / nextafterf / nextafterl
<-lang=c99>
|
Converts a floating-point number to the type of the function and calculates the representable value following the converted number on the real axis.
|
|
nexttoward / nexttowardf / nexttowardl
<-lang=c99>
|
Equivalent to the nextafter function group except that the second argument is of type long double and returns the second argument after conversion to the type of the function.
|
|
fdim / fdimf / fdiml
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates the positive difference.
|
|
fmax / fmaxf / fmaxl
<-lang=c99>
|
Obtains the greater of two values.
|
|
fmin / fminf / fminl
<-lang=c99>
|
Obtains the smaller of two values.
|
|
fma / fmaf / fmal
<-lang=c99>
|
Calculates (d1 * d2) + d3 as a single ternary operation.
|
 ).
).